G.Patton
Expert
- Joined
- Jul 5, 2021
- Messages
- 2,704
- Solutions
- 3
- Reaction score
- 2,858
- Points
- 113
- Deals
- 1
Introduction
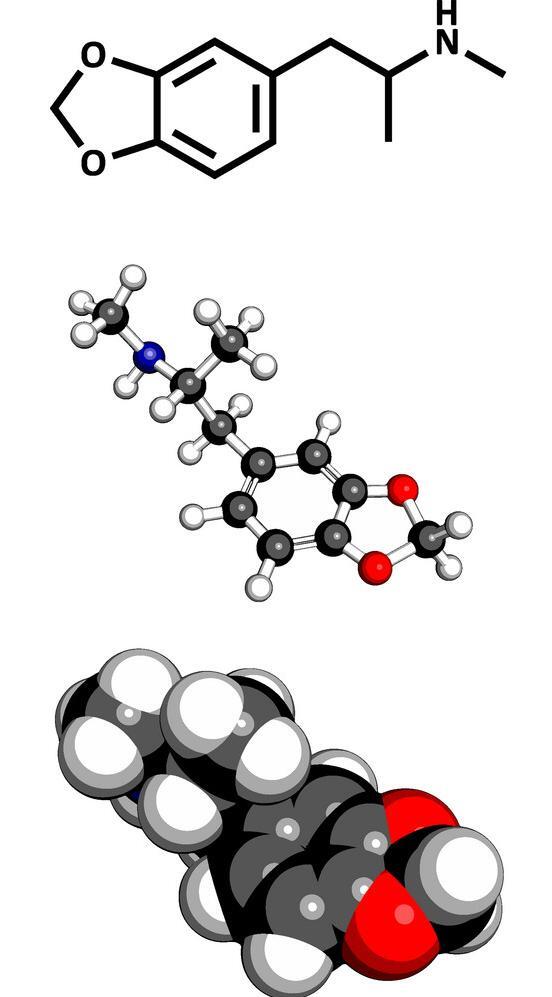
The following method shows that the NaBH4 reduction actually is superior to all other common routes used in clandestine chemistry and this method allows to scale MDMA synthesis unlike aluminum amalgam reduction. The method is quite simple, it doesn't take expensive equipment. Procedures with the reaction mixture are simple and efficient. This method is very usefull for big scale production of MDMA and gives high yields (90%+).
Difficulty rating: 5/10
Reagents:
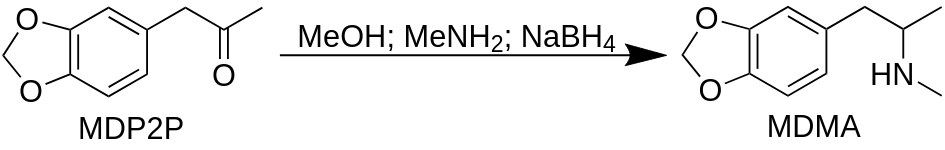 Reagents preparation
Reagents preparation
Distilled water (H2O) 8 L with 8 mL 33% HCl is added to the reaction mixture with a constant stirring. Reaction mixture is turned to greenish brown color, pH 10.5 (11 is better than 10). When green soap is started to form, it means that you've added far too much HCl. MDMA free base will settle on a reaction vessel bottom. Organic layer is drained out (separated).
DCM 200 mL is added to the reaction vessel with water layer and the mixture is stirred for 10 min. The stirrer is stopped and reaction mixture is left 30 min. DCM with the rest MDMA freebase will settle on the vessel bottom. Organic layer is drained out and extracts are combined. There is ~1750 mL of MDMA free base and DCM.
Purification
 Crystallization
Crystallization
The following method shows that the NaBH4 reduction actually is superior to all other common routes used in clandestine chemistry and this method allows to scale MDMA synthesis unlike aluminum amalgam reduction. The method is quite simple, it doesn't take expensive equipment. Procedures with the reaction mixture are simple and efficient. This method is very usefull for big scale production of MDMA and gives high yields (90%+).
There is a relatively fast formation of the imine and the imine is reduced rapidly. There's no reduction of the ketone to the secondary alcohol. In similar reactions, the water that is produced during the forming of the imine (Schiff Base) is removed from the reaction before the imine is reduced with drying salt, or molecular sieves, or by using toluene as the solvent, so the water and the toluene form an azeotrope.
Difficulty rating: 5/10
Reagents:
- Methylamine gas (MeNH2) 300 g;
- Methanol (MeOH) 3000 g;
- 3,4-Methylenedioxyphenylpropan-2-one (MDP2P; cas 4676-39-5) 1000 g;
- Sodium borohydride (NaBH4) 100 g;
- Distilled water (H2O) 8 L;
- Hydrochloric acid 8 mL 33% HCl;
- Dichloromethane (DCM) 200 mL;
- Acetone 4 L;
- Sodium hydroxide aq solution 30% (NaOH aq) 200 mL;
- Reactor 20 L, equipped with thermometer and overhead stirrer;
- Freezer;
- Retort stand and clamp for securing apparatus;
- Syringe or Pasteur pipette;
- pH indicator papers;
- Beakers (2 L x2, 1 L, 500 mL x2);
- Bucket 20-30 L;
- Vacuum source;
- Laboratory scale (1-1000 g is suitable);
- Measuring cylinders 1000 mL and 100 mL;
- Cold water bath;
- Glass rod and spatula;
- Laboratory grade thermometer;
- Buchner flask and funnel;
- Filter paper;
- Wet towel;
- Vacuum distillation kit;
- HCl gas source;
- Hose (optional);
- Heating plate or heating mantle;
Methylamine gas (MeNH2) 300 g is dissolved in chilled 3000 g methanol (MeOH; -17-20 °C) in 20 L reactor, equipped with thermometer and overhead stirrer. The mixture is cooled down to 5 °C. The stirrer is turned on and MDP2P 1000 g is added.
Notes: Methylamine (MeNH2) gas 300 g is made by reaction of methylamine hydrochloride (MeNH2*HCl) with sodium hydroxide (NaOH).
MDP2P reduction to MDMASodium borohydride (NaBH4) 100 g is added in portions, one teaspoon per ~5 min, H2 gas bubbling has to disappear before next addition (wash down with methanol). Temperature is maintain between 8-10 °C. Sodium borohydride (NaBH4) addition is taken 2-7 h. The mixture is stirred for 2 days. The stirring time can be reduced to 4 h for people in a hurry, 10-20% will be lost.
Notes: When the reaction vessel is opened it should be covered by a wet towel, so that the methylamine gas can be absorbed by the water. 1 L Water can absorb 1000 L NH3 gas. An airlock can be used for that goal as well. Do not airtight the flask, let a thin hose out the window (or a fume hood), wrapped at the end with a wet towel.
Distilled water (H2O) 8 L with 8 mL 33% HCl is added to the reaction mixture with a constant stirring. Reaction mixture is turned to greenish brown color, pH 10.5 (11 is better than 10). When green soap is started to form, it means that you've added far too much HCl. MDMA free base will settle on a reaction vessel bottom. Organic layer is drained out (separated).
DCM 200 mL is added to the reaction vessel with water layer and the mixture is stirred for 10 min. The stirrer is stopped and reaction mixture is left 30 min. DCM with the rest MDMA freebase will settle on the vessel bottom. Organic layer is drained out and extracts are combined. There is ~1750 mL of MDMA free base and DCM.
Notes: You can basify the water layer again with conc. NaOH solution to pH 13-14 and drain out MDMA free base residue again.
Purification
A vacuum distillation setup is prepared. Methanol, DCM, water and other low boiling substances are distilled off at 130 °C firstly. Then, a heater is set at 165 °C, little drops of MDMA oil are condensated and seen around 140-145 °C; at 160-165 °C (20-18 mbar) MDMA oil is distilled intensively. The clean MDMA free base distillation yield is ~ 1.0 L.
A membrane vacuum aspirator is sufficient to distill off water, methanol and other low boiling substances from the reaction mixture. A decent vacuum pump is recommended to distill MDMA free base.
A membrane vacuum aspirator is sufficient to distill off water, methanol and other low boiling substances from the reaction mixture. A decent vacuum pump is recommended to distill MDMA free base.
MDMA free base is mixed with clean, cold (-10 to -20 C), dry acetone 1:4, dry HCl gas is bubbled through this solution to reach pH 7-6.5. It have to be done carefully. A thick, white crystal mass will be formed after ~5 min bubbling. pH Have to be checked frequently with pH-meter or indicator paper. If the solution become hot, place it into a big freezer to cool it down and continue with a next cold batch. Be very careful and don't drop pH below 7 to 6.5 because MDMA*HCl crystals will dissolve again. In this case, you have to add NaOH base solution again until pH rise up to 7. At least 200 mL base have to be kept ready for spare case of mistakes. The acetone/powder mix is filtered and dried on Buchner funnel with aspirator vacuum. Then, MDMA*HCl is dried again on a Pyrex dish under A/C or a slow blowing fan flow in a dry room.
Last edited:
